Here’s a few notes on CPUID and /proc/cpuinfo. I made a table for quick
reference.
§What is CPUID?
On x86 and amd64 CPUs, there is a large swathe of differences in features available to the software. Some CPUs ship with AES encryption support, others ship with virtualization support, almost all ship with a collection of SIMD (single instruction multiple data) instructions. The name of the game is to reduce CPU execution times using specialized instructions. Gratefully, most users don’t need to think about this, credit to all the various code-paths found in their computer software; if your CPU doesn’t support particular instructions, a naive, slower implementation can fill in the gaps.
In other cases, one needs to know in order to configure embedded or low end hardware for efficient operation. When software is tightly coupled to a single sort of computer architecture, many efficiencies can be realized at a cost of software portability. For example, I am writing this article on a Pentium M laptop 20 years past its prime, yet runs modern Linux just-the-same. It can even run Firefox, albeit rather slowly. Discord will load! Part of this feat is attributed to optimizing software specifically for the quirks of this computer’s architecture: an ever-stalling instruction pipeline, a minute cache size, and a low memory environment. CPU feature detection via CPUID for legacy hardware is concerned instead with choosing effecient code paths at primarily compile time. Most of these optimizations come at a cost: the software only runs on this specific machine.
There’s another case where it helps to understand CPUID. Persnickety firmwares
covet virtualization CPU support like a it’s going out of fashion. A quick
glance at CPUID-derived diagnostics is a rite-of-passage for any
troubleshooter. If the virtualization feature isn’t in /proc/cpuinfo, then
the firmware disabled it, or the hardware simply doesn’t support
virtualization.
How do we determine what features are available at runtime or compile time?
Enter the CPUID instruction. This instruction enumerates CPU hardware features
available to software. From a developer’s perspective, all you need to do is
set the eax register (and ecx in some cases!), then execute the CPUID
instruction. See OSDev Wiki and Wikipedia for supplementary information. This is
how software can detect existence of speedy features like AVX SIMD or AES
acceleration at runtime. Utilities for configuring build environments for
generating optimized software use CPUID to detect what sort of code to generate
for the target architecture.
There are varying ways for looking up the features present on a x86 or amd64
machine and a few Linux techniques are outlined below. The easiest technique
is to look for the flags in /proc/cpuinfo — see docs.
§The CPUID Table
With hopes to understand each CPUID feature, I looked for chart of terse and
minimal content, just enough to understand what’s what. An online search
didn’t find such a chart or table. So here is a tabulated form of
tools/arch/x86/kcpuid/cpuid.csv (gitweb) as found in the 6.6.30 kernel tree.
The table isn’t exhaustive, but everything you care about is likely listed
herein.
| LEAF | SUBLEAF | register_name | bits | short_name | long_description | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | EAX | 31:0 | max_basic_leafs | Max input value for supported subleafs | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EAX | 3:0 | stepping | Stepping ID | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EAX | 7:4 | model | Model | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EAX | 11:8 | family | Family ID | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EAX | 13:12 | processor | Processor Type | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EAX | 19:16 | model_ext | Extended Model ID | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EAX | 27:20 | family_ext | Extended Family ID | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EBX | 7:0 | brand | Brand Index | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EBX | 15:8 | clflush_size | CLFLUSH line size (value * 8) in bytes | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EBX | 23:16 | max_cpu_id | Maxim number of addressable logic cpu in this package | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EBX | 31:24 | apic_id | Initial APIC ID | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 0 | sse3 | Streaming SIMD Extensions 3(SSE3) | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 1 | pclmulqdq | PCLMULQDQ instruction supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 2 | dtes64 | DS area uses 64-bit layout | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 3 | mwait | MONITOR/MWAIT supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 4 | ds_cpl | CPL Qualified Debug Store which allows for branch message storage qualified by CPL | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 5 | vmx | Virtual Machine Extensions supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 6 | smx | Safer Mode Extension supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 7 | eist | Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 8 | tm2 | Thermal Monitor 2 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 9 | ssse3 | Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSSE3) | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 10 | l1_ctx_id | L1 data cache could be set to either adaptive mode or shared mode (check IA32_MISC_ENABLE bit 24 definition) | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 11 | sdbg | IA32_DEBUG_INTERFACE MSR for silicon debug supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 12 | fma | FMA extensions using YMM state supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 13 | cmpxchg16b | ‘CMPXCHG16B - Compare and Exchange Bytes’ supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 14 | xtpr_update | xTPR Update Control supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 15 | pdcm | Perfmon and Debug Capability present | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 17 | pcid | Process-Context Identifiers feature present | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 18 | dca | Prefetching data from a memory mapped device supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 19 | sse4_1 | SSE4.1 feature present | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 20 | sse4_2 | SSE4.2 feature present | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 21 | x2apic | x2APIC supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 22 | movbe | MOVBE instruction supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 23 | popcnt | POPCNT instruction supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 24 | tsc_deadline_timer | LAPIC supports one-shot operation using a TSC deadline value | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 25 | aesni | AESNI instruction supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 26 | xsave | XSAVE/XRSTOR processor extended states (XSETBV/XGETBV/XCR0) | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 27 | osxsave | OS has set CR4.OSXSAVE bit to enable XSETBV/XGETBV/XCR0 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 28 | avx | AVX instruction supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 29 | f16c | 16-bit floating-point conversion instruction supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | ECX | 30 | rdrand | RDRAND instruction supported | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 0 | fpu | x87 FPU on chip | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 1 | vme | Virtual-8086 Mode Enhancement | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 2 | de | Debugging Extensions | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 3 | pse | Page Size Extensions | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 4 | tsc | Time Stamp Counter | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 5 | msr | RDMSR and WRMSR Support | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 6 | pae | Physical Address Extensions | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 7 | mce | Machine Check Exception | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 8 | cx8 | CMPXCHG8B instr | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 9 | apic | APIC on Chip | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 11 | sep | SYSENTER and SYSEXIT instrs | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 12 | mtrr | Memory Type Range Registers | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 13 | pge | Page Global Bit | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 14 | mca | Machine Check Architecture | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 15 | cmov | Conditional Move Instrs | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 16 | pat | Page Attribute Table | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 17 | pse36 | 36-Bit Page Size Extension | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 18 | psn | Processor Serial Number | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 19 | clflush | CLFLUSH instr | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 21 | ds | Debug Store | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 22 | acpi | Thermal Monitor and Software Controlled Clock Facilities | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 23 | mmx | Intel MMX Technology | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 24 | fxsr | XSAVE and FXRSTOR Instrs | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 25 | sse | SSE | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 26 | sse2 | SSE2 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 27 | ss | Self Snoop | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 28 | hit | Max APIC IDs | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 29 | tm | Thermal Monitor | |||||
| 1 | 0 | EDX | 31 | pbe | Pending Break Enable | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EAX | 4:0 | cache_type | Cache type like instr/data or unified | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EAX | 7:5 | cache_level | Cache Level (starts at 1) | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EAX | 8 | cache_self_init | Cache Self Initialization | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EAX | 9 | fully_associate | Fully Associative cache | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EAX | 25:14 | max_logical_id | Max number of addressable IDs for logical processors sharing the cache | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EAX | 31:26 | max_phy_id | Max number of addressable IDs for processors in phy package | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EBX | 11:0 | cache_linesize | Size of a cache line in bytes | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EBX | 21:12 | cache_partition | Physical Line partitions | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EBX | 31:22 | cache_ways | Ways of associativity | |||||
| 4 | 0 | ECX | 31:0 | cache_sets | Number of Sets - 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EDX | 0 | c_wbinvd | 1 means WBINVD/INVD is not ganranteed to act upon lower level caches of non-originating threads sharing this cache | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EDX | 1 | c_incl | Whether cache is inclusive of lower cache level | |||||
| 4 | 0 | EDX | 2 | c_comp_index | Complex Cache Indexing | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EAX | 15:0 | min_mon_size | Smallest monitor line size in bytes | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EBX | 15:0 | max_mon_size | Largest monitor line size in bytes | |||||
| 5 | 0 | ECX | 0 | mwait_ext | Enum of Monitor-Mwait extensions supported | |||||
| 5 | 0 | ECX | 1 | mwait_irq_break | Largest monitor line size in bytes | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EDX | 3:0 | c0_sub_stats | Number of C0* sub C-states supported using MWAIT | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EDX | 7:4 | c1_sub_stats | Number of C1* sub C-states supported using MWAIT | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EDX | 11:8 | c2_sub_stats | Number of C2* sub C-states supported using MWAIT | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EDX | 15:12 | c3_sub_stats | Number of C3* sub C-states supported using MWAIT | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EDX | 19:16 | c4_sub_stats | Number of C4* sub C-states supported using MWAIT | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EDX | 23:20 | c5_sub_stats | Number of C5* sub C-states supported using MWAIT | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EDX | 27:24 | c6_sub_stats | Number of C6* sub C-states supported using MWAIT | |||||
| 5 | 0 | EDX | 31:28 | c7_sub_stats | Number of C7* sub C-states supported using MWAIT | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 0 | dig_temp | Digital temperature sensor supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 1 | turbo | Intel Turbo Boost | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 2 | arat | Always running APIC timer | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 4 | pln | Power limit notifications supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 5 | ecmd | Clock modulation duty cycle extension supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 6 | ptm | Package thermal management supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 7 | hwp | HWP base register | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 8 | hwp_notify | HWP notification | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 9 | hwp_act_window | HWP activity window | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 10 | hwp_energy | HWP energy performance preference | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 11 | hwp_pkg_req | HWP package level request | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 13 | hdc | HDC base registers supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 14 | turbo3 | Turbo Boost Max 3.0 | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 15 | hwp_cap | Highest Performance change supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 16 | hwp_peci | HWP PECI override is supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 17 | hwp_flex | Flexible HWP is supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 18 | hwp_fast | Fast access mode for the IA32_HWP_REQUEST MSR is supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EAX | 20 | hwp_ignr | Ignoring Idle Logical Processor HWP request is supported | |||||
| 6 | 0 | EBX | 3:0 | therm_irq_thresh | Number of Interrupt Thresholds in Digital Thermal Sensor | |||||
| 6 | 0 | ECX | 0 | aperfmperf | Presence of IA32_MPERF and IA32_APERF | |||||
| 6 | 0 | ECX | 3 | energ_bias | Performance-energy bias preference supported | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 0 | fsgsbase | RDFSBASE/RDGSBASE/WRFSBASE/WRGSBASE supported | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 1 | tsc_adjust | TSC_ADJUST MSR supported | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 2 | sgx | Software Guard Extensions | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 3 | bmi1 | BMI1 | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 4 | hle | Hardware Lock Elision | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 5 | avx2 | AVX2 | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 7 | smep | Supervisor-Mode Execution Prevention | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 8 | bmi2 | BMI2 | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 9 | rep_movsb | Enhanced REP MOVSB/STOSB | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 10 | invpcid | INVPCID instruction | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 11 | rtm | Restricted Transactional Memory | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 12 | rdt_m | Intel RDT Monitoring capability | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 13 | depc_fpu_cs_ds | Deprecates FPU CS and FPU DS | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 14 | mpx | Memory Protection Extensions | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 15 | rdt_a | Intel RDT Allocation capability | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 16 | avx512f | AVX512 Foundation instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 17 | avx512dq | AVX512 Double and Quadword AVX512 instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 18 | rdseed | RDSEED instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 19 | adx | ADX instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 20 | smap | Supervisor Mode Access Prevention | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 21 | avx512ifma | AVX512 Integer Fused Multiply Add | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 23 | clflushopt | CLFLUSHOPT instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 24 | clwb | CLWB instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 25 | intel_pt | Intel Processor Trace instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 26 | avx512pf | Prefetch | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 27 | avx512er | AVX512 Exponent Reciproca instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 28 | avx512cd | AVX512 Conflict Detection instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 29 | sha | Intel Secure Hash Algorithm Extensions instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 30 | avx512bw | AVX512 Byte & Word instr | |||||
| 7 | 0 | EBX | 31 | avx512vl | AVX512 Vector Length Extentions (VL) | |||||
| 7 | 0 | ECX | 0 | prefetchwt1 | X | |||||
| 7 | 0 | ECX | 1 | avx512vbmi | AVX512 Vector Byte Manipulation Instructions | |||||
| 7 | 0 | ECX | 2 | umip | User-mode Instruction Prevention | |||||
| 7 | 0 | ECX | 3 | pku | Protection Keys for User-mode pages | |||||
| 7 | 0 | ECX | 4 | ospke | CR4 PKE set to enable protection keys | |||||
| 7 | 0 | ECX | 21:17 | mawau | The value of MAWAU used by the BNDLDX and BNDSTX instructions in 64-bit mode | |||||
| 7 | 0 | ECX | 22 | rdpid | RDPID and IA32_TSC_AUX | |||||
| 7 | 0 | ECX | 30 | sgx_lc | SGX Launch Configuration | |||||
| 9 | 0 | ECX | 31:0 | dca_cap | The value of IA32_PLATFORM_DCA_CAP | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EAX | 7:0 | pmu_ver | Performance Monitoring Unit version | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EAX | 15:8 | pmu_gp_cnt_num | Numer of general-purose PMU counters per logical CPU | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EAX | 23:16 | pmu_cnt_bits | Bit wideth of PMU counter | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EAX | 31:24 | pmu_ebx_bits | Length of EBX bit vector to enumerate PMU events | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EBX | 0 | pmu_no_core_cycle_evt | Core cycle event not available | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EBX | 1 | pmu_no_instr_ret_evt | Instruction retired event not available | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EBX | 2 | pmu_no_ref_cycle_evt | Reference cycles event not available | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EBX | 3 | pmu_no_llc_ref_evt | Last-level cache reference event not available | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EBX | 4 | pmu_no_llc_mis_evt | Last-level cache misses event not available | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EBX | 5 | pmu_no_br_instr_ret_evt | Branch instruction retired event not available | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | EBX | 6 | pmu_no_br_mispredict_evt | Branch mispredict retired event not available | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | ECX | 4:0 | pmu_fixed_cnt_num | Performance Monitoring Unit version | |||||
| 0xA | 0 | ECX | 12:5 | pmu_fixed_cnt_bits | Numer of PMU counters per logical CPU | |||||
| 0xB | 0 | EAX | 4:0 | id_shift | Number of bits to shift right on x2APIC ID to get a unique topology ID of the next level type | |||||
| 0xB | 0 | EBX | 15:0 | cpu_nr | Number of logical processors at this level type | |||||
| 0xB | 0 | ECX | 15:8 | lvl_type | 0-Invalid 1-SMT 2-Core | |||||
| 0xB | 0 | EDX | 31:0 | x2apic_id | x2APIC ID the current logical processor | |||||
| 0xD | 0 | EAX | 0 | x87 | X87 state | |||||
| 0xD | 0 | EAX | 1 | sse | SSE state | |||||
| 0xD | 0 | EAX | 2 | avx | AVX state | |||||
| 0xD | 0 | EAX | 4:3 | mpx | MPX state | |||||
| 0xD | 0 | EAX | 7:5 | avx512 | AVX-512 state | |||||
| 0xD | 0 | EAX | 9 | pkru | PKRU state | |||||
| 0xD | 0 | EBX | 31:0 | max_sz_xcr0 | Maximum size (bytes) required by enabled features in XCR0 | |||||
| 0xD | 0 | ECX | 31:0 | max_sz_xsave | Maximum size (bytes) of the XSAVE/XRSTOR save area | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | EAX | 0 | xsaveopt | XSAVEOPT available | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | EAX | 1 | xsavec | XSAVEC and compacted form supported | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | EAX | 2 | xgetbv | XGETBV supported | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | EAX | 3 | xsaves | XSAVES/XRSTORS and IA32_XSS supported | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | EBX | 31:0 | max_sz_xcr0 | Maximum size (bytes) required by enabled features in XCR0 | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | ECX | 8 | pt | PT state | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | ECX | 11 | cet_usr | CET user state | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | ECX | 12 | cet_supv | CET supervisor state | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | ECX | 13 | hdc | HDC state | |||||
| 0xD | 1 | ECX | 16 | hwp | HWP state | |||||
| 0xF | 0 | EBX | 31:0 | rmid_range | Maximum range (zero-based) of RMID within this physical processor of all types | |||||
| 0xF | 0 | EDX | 1 | l3c_rdt_mon | L3 Cache RDT Monitoring supported | |||||
| 0xF | 1 | ECX | 31:0 | rmid_range | Maximum range (zero-based) of RMID of this types | |||||
| 0xF | 1 | EDX | 0 | l3c_ocp_mon | L3 Cache occupancy Monitoring supported | |||||
| 0xF | 1 | EDX | 1 | l3c_tbw_mon | L3 Cache Total Bandwidth Monitoring supported | |||||
| 0xF | 1 | EDX | 2 | l3c_lbw_mon | L3 Cache Local Bandwidth Monitoring supported | |||||
| 0x10 | 0 | EBX | 1 | l3c_rdt_alloc | L3 Cache Allocation supported | |||||
| 0x10 | 0 | EBX | 2 | l2c_rdt_alloc | L2 Cache Allocation supported | |||||
| 0x10 | 0 | EBX | 3 | mem_bw_alloc | Memory Bandwidth Allocation supported | |||||
| 0x12 | 0 | EAX | 0 | sgx1 | L3 Cache Allocation supported | |||||
| 0x12 | 1 | EAX | 0 | sgx2 | L3 Cache Allocation supported | |||||
| 0x15 | 0 | EAX | 31:0 | tsc_denominator | The denominator of the TSC/”core crystal clock” ratio | |||||
| 0x15 | 0 | EBX | 31:0 | tsc_numerator | The numerator of the TSC/”core crystal clock” ratio | |||||
| 0x15 | 0 | ECX | 31:0 | nom_freq | Nominal frequency of the core crystal clock in Hz | |||||
| 0x16 | 0 | EAX | 15:0 | cpu_base_freq | Processor Base Frequency in MHz | |||||
| 0x16 | 0 | EBX | 15:0 | cpu_max_freq | Maximum Frequency in MHz | |||||
| 0x16 | 0 | ECX | 15:0 | bus_freq | Bus (Reference) Frequency in MHz | |||||
| 0x17 | 0 | EAX | 31:0 | max_socid | Maximum input value of supported sub-leaf | |||||
| 0x17 | 0 | EBX | 15:0 | soc_vid | SOC Vendor ID | |||||
| 0x17 | 0 | EBX | 16 | std_vid | SOC Vendor ID is assigned via an industry standard scheme | |||||
| 0x17 | 0 | ECX | 31:0 | soc_pid | SOC Project ID assigned by vendor | |||||
| 0x17 | 0 | EDX | 31:0 | soc_sid | SOC Stepping ID | |||||
| 0x1A | 0 | EAX | 31:24 | core_type | 20H-Intel_Atom 40H-Intel_Core | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EAX | 27:20 | extfamily | Extended family | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EAX | 19:16 | extmodel | Extended model | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EAX | 11:8 | basefamily | Description of Family | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EAX | 11:8 | basemodel | Model numbers vary with product | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EAX | 3:0 | stepping | Processor stepping (revision) for a specific model | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EBX | 31:28 | pkgtype | Specifies the package type | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 0 | lahf_lm | LAHF/SAHF available in 64-bit mode | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 1 | cmplegacy | Core multi-processing legacy mode | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 2 | svm | Indicates support for: VMRUN | VMLOAD | VMSAVE | CLGI | VMMCALL | and INVLPGA |
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 3 | extapicspace | Extended APIC register space | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 4 | altmovecr8 | Indicates support for LOCK MOV CR0 means MOV CR8 | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 5 | lzcnt | LZCNT | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 6 | sse4a | EXTRQ | INSERTQ | MOVNTSS | and MOVNTSD instruction support | ||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 7 | misalignsse | Misaligned SSE Mode | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 8 | prefetchw | PREFETCHW | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 9 | osvw | OS Visible Work-around support | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 10 | ibs | Instruction Based Sampling | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 11 | xop | Extended operation support | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 12 | skinit | SKINIT and STGI support | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 13 | wdt | Watchdog timer support | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 15 | lwp | Lightweight profiling support | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 16 | fma4 | Four-operand FMA instruction support | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 17 | tce | Translation cache extension | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 22 | TopologyExtensions | Indicates support for Core::X86::Cpuid::CachePropEax0 and Core::X86::Cpuid::ExtApicId | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 23 | perfctrextcore | Indicates support for Core::X86::Msr::PERF_CTL0 - 5 and Core::X86::Msr::PERF_CTR | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 24 | perfctrextdf | Indicates support for Core::X86::Msr::DF_PERF_CTL and Core::X86::Msr::DF_PERF_CTR | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 26 | databreakpointextension | Indicates data breakpoint support for Core::X86::Msr::DR0_ADDR_MASK | Core::X86::Msr::DR1_ADDR_MASK | Core::X86::Msr::DR2_ADDR_MASK and Core::X86::Msr::DR3_ADDR_MASK | |||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 27 | perftsc | Performance time-stamp counter supported | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 28 | perfctrextllc | Indicates support for L3 performance counter extensions | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 29 | mwaitextended | MWAITX and MONITORX capability is supported | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | ECX | 30 | admskextn | Indicates support for address mask extension (to 32 bits and to all 4 DRs) for instruction breakpoints | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 0 | fpu | x87 floating point unit on-chip | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 1 | vme | Virtual-mode enhancements | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 2 | de | Debugging extensions | IO breakpoints | CR4.DE | |||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 3 | pse | Page-size extensions (4 MB pages) | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 4 | tsc | Time stamp counter | RDTSC/RDTSCP instructions | CR4.TSD | |||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 5 | msr | Model-specific registers (MSRs) | with RDMSR and WRMSR instructions | ||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 6 | pae | Physical-address extensions (PAE) | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 7 | mce | Machine Check Exception | CR4.MCE | ||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 8 | cmpxchg8b | CMPXCHG8B instruction | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 9 | apic | advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) exists and is enabled | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 11 | sysret | SYSCALL/SYSRET supported | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 12 | mtrr | Memory-type range registers | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 13 | pge | Page global extension | CR4.PGE | ||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 14 | mca | Machine check architecture | MCG_CAP | ||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 15 | cmov | Conditional move instructions | CMOV | FCOMI | FCMOV | ||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 16 | pat | Page attribute table | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 17 | pse36 | Page-size extensions | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 20 | exec_dis | Execute Disable Bit available | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 22 | mmxext | AMD extensions to MMX instructions | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 23 | mmx | MMX instructions | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 24 | fxsr | FXSAVE and FXRSTOR instructions | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 25 | ffxsr | FXSAVE and FXRSTOR instruction optimizations | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 26 | 1gb_page | 1GB page supported | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 27 | rdtscp | RDTSCP and IA32_TSC_AUX are available | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 29 | lm | 64b Architecture supported | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 30 | threednowext | AMD extensions to 3DNow! instructions | |||||
| 0x80000001 | 0 | EDX | 31 | threednow | 3DNow! instructions | |||||
| 0x80000006 | 0 | ECX | 7:0 | clsize | Cache Line size in bytes | |||||
| 0x80000006 | 0 | ECX | 15:12 | l2c_assoc | L2 Associativity | |||||
| 0x80000006 | 0 | ECX | 31:16 | csize | Cache size in 1K units | |||||
| 0x80000007 | 0 | EDX | 8 | nonstop_tsc | Invariant TSC available | |||||
| 0x80000008 | 0 | EAX | 7:0 | phy_adr_bits | Physical Address Bits | |||||
| 0x80000008 | 0 | EAX | 15:8 | lnr_adr_bits | Linear Address Bits | |||||
| 0x80000007 | 0 | EBX | 9 | wbnoinvd | WBNOINVD | |||||
| 0x8000001E | 0 | EAX | 31:0 | extended_apic_id | Extended APIC ID | |||||
| 0x8000001E | 0 | EBX | 7:0 | core_id | Identifies the logical core ID | |||||
| 0x8000001E | 0 | EBX | 15:8 | threads_per_core | The number of threads per core is threads_per_core + 1 | |||||
| 0x8000001E | 0 | ECX | 7:0 | node_id | Node ID | |||||
| 0x8000001E | 0 | ECX | 10:8 | nodes_per_processor | Nodes per processor { 0: 1 node | else reserved } | ||||
| 0x8000001F | 0 | EAX | 0 | sme | Secure Memory Encryption | |||||
| 0x8000001F | 0 | EAX | 1 | sev | Secure Encrypted Virtualization | |||||
| 0x8000001F | 0 | EAX | 2 | vmpgflush | VM Page Flush MSR | |||||
| 0x8000001F | 0 | EAX | 3 | seves | SEV Encrypted State | |||||
| 0x8000001F | 0 | EBX | 5:0 | c-bit | Page table bit number used to enable memory encryption | |||||
| 0x8000001F | 0 | EBX | 11:6 | mem_encrypt_physaddr_width | Reduction of physical address space in bits with SME enabled | |||||
| 0x8000001F | 0 | ECX | 31:0 | num_encrypted_guests | Maximum ASID value that may be used for an SEV-enabled guest | |||||
| 0x8000001F | 0 | EDX | 31:0 | minimum_sev_asid | Minimum ASID value that must be used for an SEV-enabled | SEV-ES-disabled guest |
§About the columns
- LEAF
- the value to set register
eaxprior to executing thecpuid
instruction.
- SUBLEAF
- the value to set register
ecxprior to executing thecpuidinstruction. It appears thecpuidinstruction looks inecxonly in certain cases. Read the vendor documentation for further explaination. - register_name
- the register containing the bits after
cpuidexecution - bits
- which range or single bit position to extract from register_name
- short_name
- short symbolic name. Roughly correlates with
/proc/cpuinfo - long_description
- a few words describing the CPUID entry
§How did I generate this table?
All in Emacs.
- Visit
cpuid.csvthen copy it.C-x h(mark-whole-buffer),M-w(kill-ring-save). - Visit your target org-mode file.
- Paste
C-y(yank), Uncomment the commented “key” line that has the column names in it, then move your cursor to the beginning of the first pasted line. - then mark the entire pasted text.
C-space(set-mark-command) followed byC-x C-x(exchange-point-and-mark) might work. - Delete unwanted lines
M-x flush-lines RET ^#\|^$ RET. - Convert the CSV to an org-mode table
C-u C-c |(org-table-create-or-convert-from-region) - That’s it.
§Other tables on the net
There are other CPUID tables online, but they didn’t quite meet my needs of compactness.
- The Wikipedia CPUID article offers a detailed breakdown of all the features
- The Intel datasheet, AMD datasheet, and additional resources hyperlinked in the aforementioned Wikipedia CPUID article’s References, Further reading, and External links sections.
- Bunch of others discoverable via Google that are quite detailed.
§A few ways to display CPUID feature flags
§/proc/cpuinfo
In the following example see the flags field. This approach requires no
external tooling, only a booted Linux kernel. The cinch is one has to
correlate the short-names with descriptions or have a brilliant memory.
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 9
model name : Intel(R) Pentium(R) M processor 1600MHz
stepping : 5
microcode : 0x7
cpu MHz : 1600.000
cache size : 1024 KB
physical id : 0
siblings : 1
core id : 0
cpu cores : 1
apicid : 0
initial apicid : 0
fdiv_bug : no
f00f_bug : no
coma_bug : no
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 2
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr mce cx8 sep mtrr pge mca cmov clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 tm pbe bts cpuid est tm2
bugs : cpu_meltdown spectre_v1 spectre_v2 spec_store_bypass l1tf mds swapgs itlb_multihit mmio_unknown
bogomips : 3198.33
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 32 bits physical, 32 bits virtual
power management:
§lscpu
lscpu seems to provide the same information as the above, but with a slimmer
output. util-linux provides this package on most distros, so it’s oft
installed out of the box.
$ lscpu
Architecture: i686
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit
Address sizes: 32 bits physical, 32 bits virtual
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 1
On-line CPU(s) list: 0
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
Model name: Intel(R) Pentium(R) M processor 1600MHz
CPU family: 6
Model: 9
Thread(s) per core: 1
Core(s) per socket: 1
Socket(s): 1
Stepping: 5
CPU(s) scaling MHz: 100%
CPU max MHz: 1600.0000
CPU min MHz: 600.0000
BogoMIPS: 3198.33
Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr mce cx8 sep mtrr pge mca cmov clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 tm pbe bts cpuid est tm2
Vulnerability Gather data sampling: Not affected
Vulnerability Itlb multihit: KVM: Mitigation: VMX unsupported
Vulnerability L1tf: Vulnerable
Vulnerability Mds: Vulnerable: Clear CPU buffers attempted, no microcode; SMT disabled
Vulnerability Meltdown: Vulnerable
Vulnerability Mmio stale data: Unknown: No mitigations
Vulnerability Retbleed: Not affected
Vulnerability Spec rstack overflow: Not affected
Vulnerability Spec store bypass: Vulnerable
Vulnerability Spectre v1: Mitigation; usercopy/swapgs barriers and __user pointer sanitization
Vulnerability Spectre v2: Mitigation; Retpolines, STIBP disabled, RSB filling, PBRSB-eIBRS Not affected
Vulnerability Srbds: Not affected
Vulnerability Tsx async abort: Not affected
§cpuid
cpuid provides a verbose output with descriptions of all CPUID feature flags.
Great if one can install an additional software package available on most distros.
$ cpuid
CPU 0:
vendor_id = "GenuineIntel"
version information (1/eax):
processor type = primary processor (0)
family = 0x6 (6)
model = 0x9 (9)
stepping id = 0x5 (5)
extended family = 0x0 (0)
extended model = 0x0 (0)
(family synth) = 0x6 (6)
(model synth) = 0x9 (9)
miscellaneous (1/ebx):
process local APIC physical ID = 0x0 (0)
maximum IDs for CPUs in pkg = 0x0 (0)
CLFLUSH line size = 0x8 (8)
brand index = 0x16 (22)
brand id = 0x16 (22): Intel Pentium M, .13um
feature information (1/edx):
x87 FPU on chip = true
VME: virtual-8086 mode enhancement = true
DE: debugging extensions = true
PSE: page size extensions = true
TSC: time stamp counter = true
RDMSR and WRMSR support = true
PAE: physical address extensions = false
MCE: machine check exception = true
CMPXCHG8B inst. = true
APIC on chip = false
SYSENTER and SYSEXIT = true
MTRR: memory type range registers = true
PTE global bit = true
MCA: machine check architecture = true
CMOV: conditional move/compare instr = true
PAT: page attribute table = true
PSE-36: page size extension = false
PSN: processor serial number = false
CLFLUSH instruction = true
DS: debug store = true
ACPI: thermal monitor and clock ctrl = true
MMX Technology = true
FXSAVE/FXRSTOR = true
SSE extensions = true
SSE2 extensions = true
SS: self snoop = false
hyper-threading / multi-core supported = false
TM: therm. monitor = true
IA64 = false
PBE: pending break event = true
feature information (1/ecx):
PNI/SSE3: Prescott New Instructions = false
PCLMULDQ instruction = false
DTES64: 64-bit debug store = false
MONITOR/MWAIT = false
CPL-qualified debug store = false
VMX: virtual machine extensions = false
SMX: safer mode extensions = false
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology = true
TM2: thermal monitor 2 = true
SSSE3 extensions = false
context ID: adaptive or shared L1 data = false
SDBG: IA32_DEBUG_INTERFACE = false
FMA instruction = false
CMPXCHG16B instruction = false
xTPR disable = false
PDCM: perfmon and debug = false
PCID: process context identifiers = false
DCA: direct cache access = false
SSE4.1 extensions = false
SSE4.2 extensions = false
x2APIC: extended xAPIC support = false
MOVBE instruction = false
POPCNT instruction = false
time stamp counter deadline = false
AES instruction = false
XSAVE/XSTOR states = false
OS-enabled XSAVE/XSTOR = false
AVX: advanced vector extensions = false
F16C half-precision convert instruction = false
RDRAND instruction = false
hypervisor guest status = false
cache and TLB information (2):
0xb0: instruction TLB: 4K, 4-way, 128 entries
0xb3: data TLB: 4K pages, 4-way, 128 entries
0x02: instruction TLB: 4M pages, 4-way, 2 entries
0x87: L2 cache: 1M, 8-way, 64 byte lines
0x30: L1 cache: 32K, 8-way, 64 byte lines
0x04: data TLB: 4M pages, 4-way, 8 entries
0x2c: L1 data cache: 32K, 8-way, 64 byte lines
extended feature flags (0x80000001/edx):
SYSCALL and SYSRET instructions = false
execution disable = false
1-GB large page support = false
RDTSCP = false
64-bit extensions technology available = false
Intel feature flags (0x80000001/ecx):
LAHF/SAHF supported in 64-bit mode = false
LZCNT advanced bit manipulation = false
3DNow! PREFETCH/PREFETCHW instructions = false
brand = " Intel(R) Pentium(R) M processor 1600MHz"
(instruction supported synth):
MWAIT = false
(multi-processing synth) = none
(multi-processing method) = Intel leaf 1
(uarch synth) = Intel {P6 Pentium M}, .13um
(synth) = Intel Pentium M (Banias B1) {P6 Pentium M}, .13um
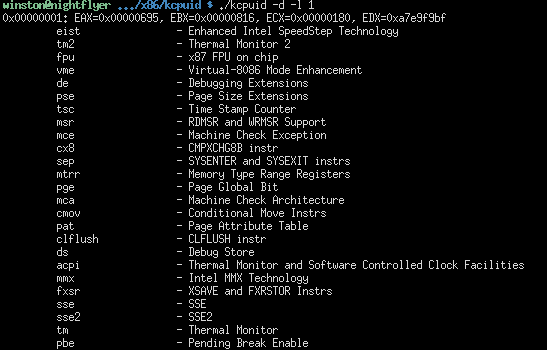
§kcpuid (in kernel tree)
kcpuid is a small utility shipped with the Linux kernel tree in directory
tools/arch/x86/kcpuid (gitweb). It appears installable with make install,
though one can run it in-place:
$ cd tools/arch/x86/kcpuid
$ make
cc -Wextra -O2 -Wall -I../../../include -o kcpuid kcpuid.c
$./kcpuid -d
CPU features:
=============
CPUID_0x0_ECX[0x0]:
EBX: 0x756e6547
ECX: 0x6c65746e
EDX: 0x49656e69
CPUID_0x1_ECX[0x0]:
eist - Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology
tm2 - Thermal Monitor 2
fpu - x87 FPU on chip
vme - Virtual-8086 Mode Enhancement
de - Debugging Extensions
pse - Page Size Extensions
tsc - Time Stamp Counter
msr - RDMSR and WRMSR Support
mce - Machine Check Exception
cx8 - CMPXCHG8B instr
sep - SYSENTER and SYSEXIT instrs
mtrr - Memory Type Range Registers
pge - Page Global Bit
mca - Machine Check Architecture
cmov - Conditional Move Instrs
pat - Page Attribute Table
clflush - CLFLUSH instr
ds - Debug Store
acpi - Thermal Monitor and Software Controlled Clock Facilities
mmx - Intel MMX Technology
fxsr - XSAVE and FXRSTOR Instrs
sse - SSE
sse2 - SSE2
tm - Thermal Monitor
pbe - Pending Break Enable
CPUID_0x2_ECX[0x0]:
EAX: 0x02b3b001
EBX: 0x00000000
ECX: 0x00000000
EDX: 0x2c043087
CPUID_0x80000000_ECX[0x0]:
EAX: 0x80000004
EBX: 0x00000000
ECX: 0x00000000
EDX: 0x00000000
CPUID_0x80000002_ECX[0x0]:
EAX: 0x20202020
EBX: 0x20202020
ECX: 0x65746e49
EDX: 0x2952286c
CPUID_0x80000003_ECX[0x0]:
EAX: 0x6e655020
EBX: 0x6d756974
ECX: 0x20295228
EDX: 0x7270204d
CPUID_0x80000004_ECX[0x0]:
EAX: 0x7365636f
EBX: 0x20726f73
ECX: 0x30303631
EDX: 0x007a484d
§Conclusion
CPUID is an interesting x86 instruction for it does nothing, but tell a tale of what the gear can do, if given the right software. Published on a 20 year old computer using a modern publishing workflow, thanks to the right software and CPUID detected CPU features.